- what we will do
- create a backend using FastAPI (Python)
- the frontend will be React that loads and displays data from the backend, and allows the user to delete items
- using easy-peasy Redux for the state management
- we will create both the frontend and backend in the same directory
- so while this is a tutorial to demonstrate various technologies that work together
- this is also a practical project that you could use as a local application
- all files are in one directory so it feels more like an application than a website with a separate backend and frontend
- recording notes
- consider for presentation: instead editing readme, change index.html and show with browser
- finished application will work like this
- what you will learn
- we will build the backend from beginning to end, so you will learn practical FastAPI
- the backend uses Python so you wll get good practical experience with that, setting up a virtual environment, etc.
- for the frontend, I will use a template that already has React set up with React Router, Tailwind, TypeScript and Easy-Peasy Redux
- I'll explain these parts a bit but we won't be setting up the frontend from scratch
- you will learn how to get the frontend and backend of a fullstack app to work together, including resolving CORS issues
- concepts, tools and programming practices included in this tutorial:
- we use TypeScript unknown for external data that is truly unknown
- a good habit for avoiding the use of any in TypeScript
- we use the library Zod to validate our external data
- and we infer our TypeScript types directly from our Zod schemas, a nice Zod/TypeScript pattern
- with Zod, we know that data which enters our app from an external source is 100% valid
- because we build a dataModel which fetches asynchronous data
- we create a function that returns a Promise
- a nice skill to know
- we style with Tailwind
- we use TypeScript unknown for external data that is truly unknown
- what we won't cover
- we won't program complete CRUD, just read and delete
- but setting up these routes in the FastAPI backend will teach you the basics to continue on with POST/PUT/PATCH routes and using these from the frontend
- we won't deploy this online
- for that you would likely want to split the frontend and backend into two projects and host them separately
- we won't set up the frontend from scratch, but will use a template that has everything set up and working
- Vite React with TypeScript
- React Router
- easy-peasy
- Tailwind
- the site is also fully responsive, works on a smartphone with responsive menu
- we won't program complete CRUD, just read and delete
- what you will have at the end of this tutorial
- a local app with a JSON data source that you can use to manage any kind of data
- having data in JSON format for local apps is useful since the data can be easily edited with a text editor like Notepad++ or in VSCode
- the frontend and backend of the fullstack website are all in one directory so self-contained like a local app
- this app will work on Windows, Mac or Linux
- we will make the backend so that it can easily have a different datasource built in, e.g. if you wanted to save the data to an SQL database instead of JSON files
- a local app with a JSON data source that you can use to manage any kind of data
- assumptions
- you have Python installed
- my version is 3.12.2 on Windows
- you are using Windows, Mac or Linux
- you have VSCode installed or some other editor
- you know React basics
- since we use a template to set up the frontend, there is a lot assumed that you know how it works
- you don't necessarily have to know Python
- I go through every step for setting up the backend, including setting up the virtual environment
- you have Python installed
- code is here
- >>> 1. setup FastAPI backend with hello-world route
- go to the directory where you have your projects, e.g. mine is currently: C:\edward\learn2025
- in that directory, create a directory with the name of your project
mkdir react-fastapi-infosite-001
- open VSCode with that directory as the root
code react-fastapi-infosite-001
- since this is a Python project, we need to create a virtual directory
python -m venv env
- activate the virtual environment
source env/Scripts/activate
- install FastAPI
pip install fastapi[all](about 40 seconds)
- create main.py
- from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/")async def hello_world():return {"message": "hello world"}
- make script to start server: serve.sh
- #!/bin/bashuvicorn main:app --reload --port 3355
- execute the serve command:
./serve.sh- you will see that it is running on localhost at the port you specified
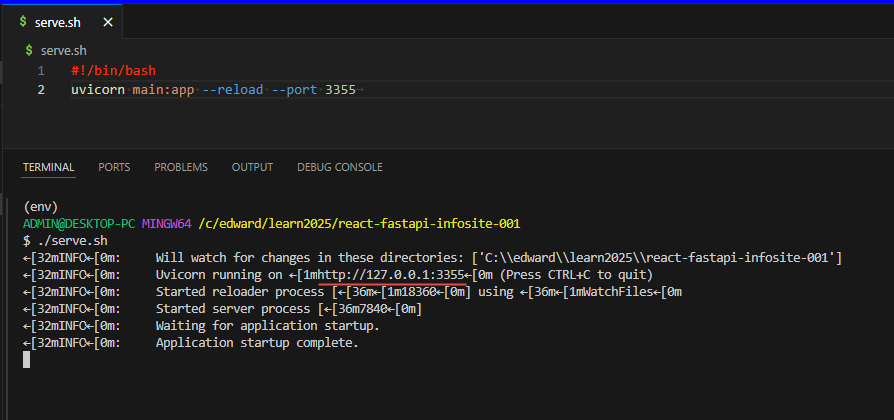
- in your browser, go to that port: ../localhost:3355http://localhost:3355
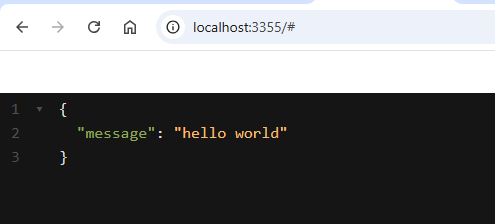
- in Postman, send a GET request to the same address:
- >>> 2. setup Git and push to a repository at GitHub
- we want to work with Git and have a backup and public version at GitHub
- open up new terminal in VSCode
- set up a local Git repository with a dev branch
git init -b dev
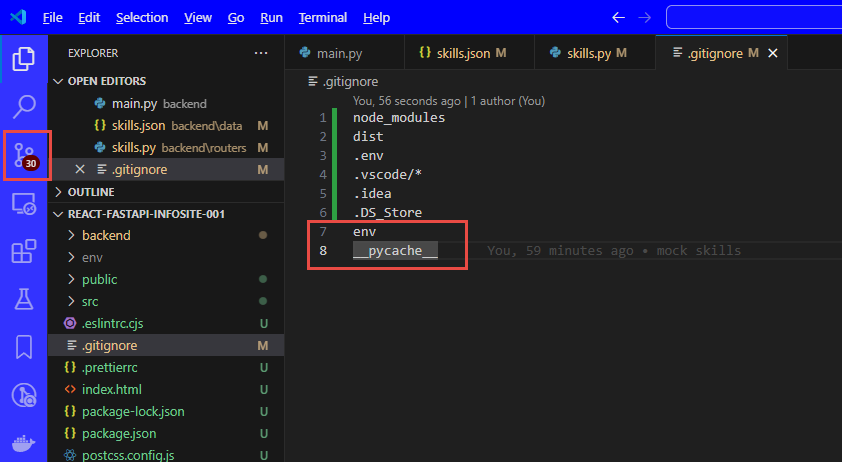
- since we now have 3000+ file to check in because of all the files in env, let's ignore it
- create **.gitignore* (ignore pycache directories as well, these will be created automatically and should not be checked into your repository)
- env__pycache__
- you now have 4 files to check in
- check this in with VSCode
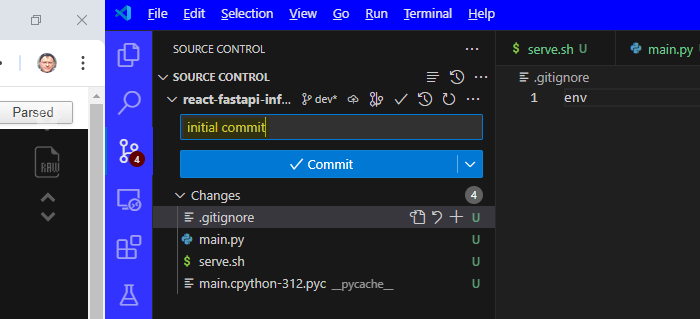
- click Public to branch
- select publish to public directory
- you now have your project as a repository at your GitHub
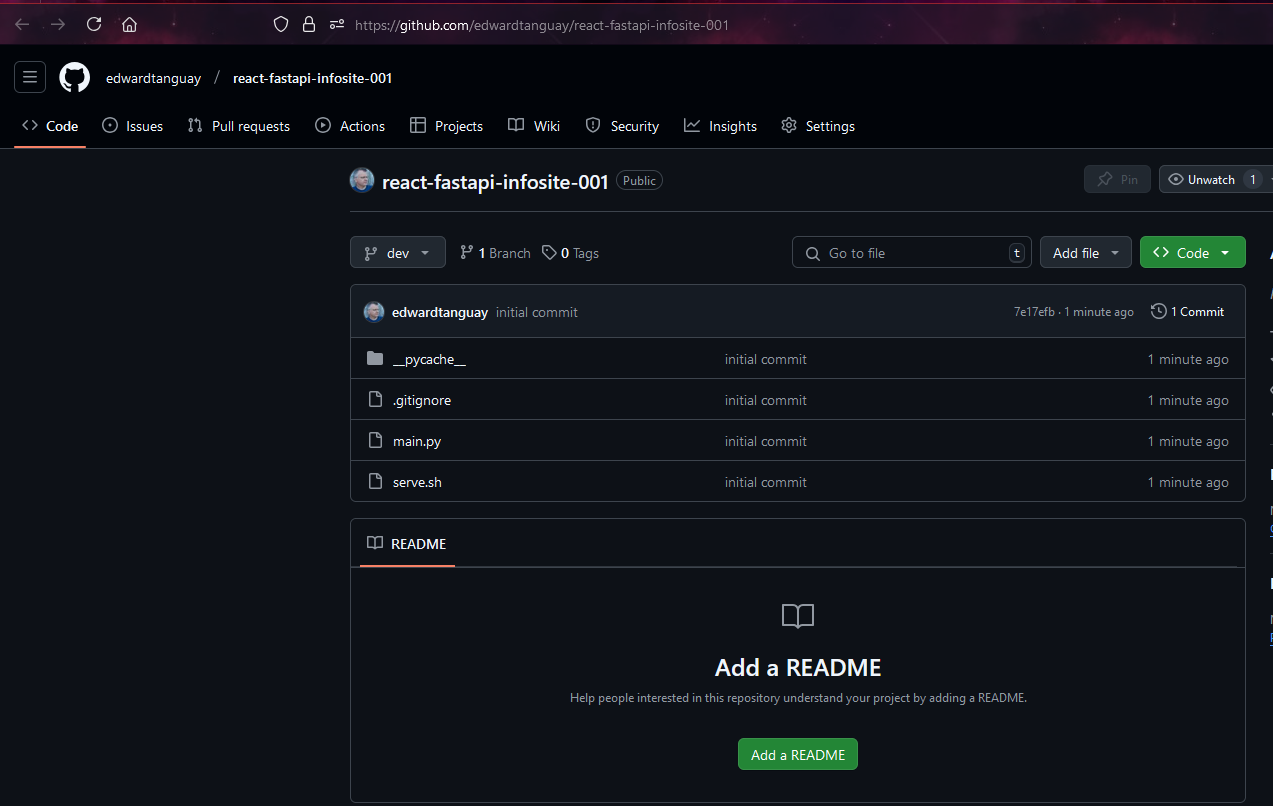
- >>> 3. create JSON data file and all GET routes to fetch data from it
- since we are going to have the frontend in this directory as well
- let's create a directory for the backend and move the current backend files to it
- make directory /backend
- move main.py and serve.sh to it
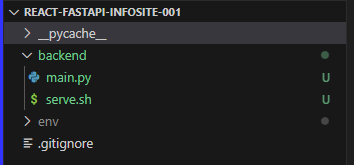
- start the server again
- from root
cd backend./serve.sh
- test it in Postman to make sure it still serves
- from root
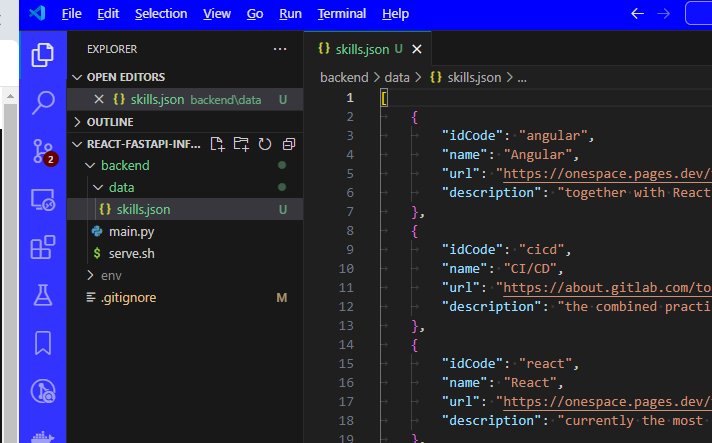
- create file /backend/data/skills.json
- add this content to it: ../skills_with_id.jsonhttps://edwardtanguay.vercel.app/share/skills_with_id.json
- you should have a file like this:
- we want to have all routes for skills in its own file
- backend/routers/skills.py
- import jsonfrom fastapi import APIRouterrouter = APIRouter(prefix="/skills")@router.get("/")async def get_skills():with open("data/skills.json", "r") as file:skills = json.load(file)return skills
- add to backend/main.py
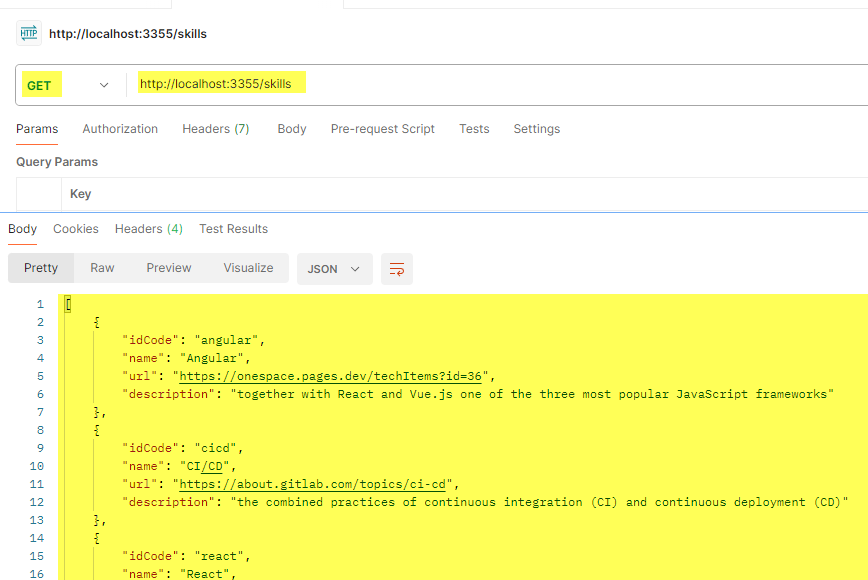
- from routers import skillsapp.include_router(skills.router)
- in Postman, you should now be able to fetch the skills:
- now add the route to fetch a single skill
- add to backend/routers/skills.py
- from fastapi import APIRouter, HTTPException, status@router.get("/{id}")async def get_skill(id:int):with open("data/skills.json", "r") as file:skills = json.load(file)try:skill = next(skill for skill in skills if skill["id"] == id)return skillexcept:raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_404_NOT_FOUND, detail="skill not found")
- add to backend/routers/skills.py
- since we are going to have the frontend in this directory as well
- >>> 4. create base frontend React site inside directory with backend
- now that we have a backend that returns data, let's make the front end to consume and display this data
- to save time on the frontend, we will use a React template site that already has numerous features installed
- since we ultimately want to have backend and frontend in the same directory
- and since we already have a directory with a backend and Git repository
- we can't simply clone this site, or create a site based on this template
- therefore we will download the files from this frontend and add them to our directory
- go to: ../vite-react-menu-createbrowserrouter-easypeasyhttps://github.com/edwardtanguay/vite-react-menu-createbrowserrouter-easypeasy
- click Code and Download ZIP
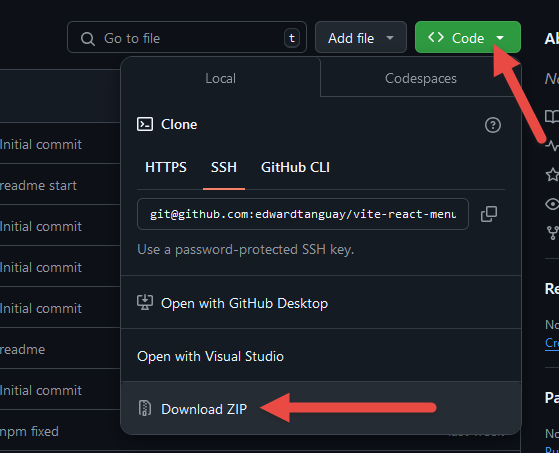
- click Code and Download ZIP
- in your file explorer, enter the zip file, select all the files, and press CTRL-C for copy
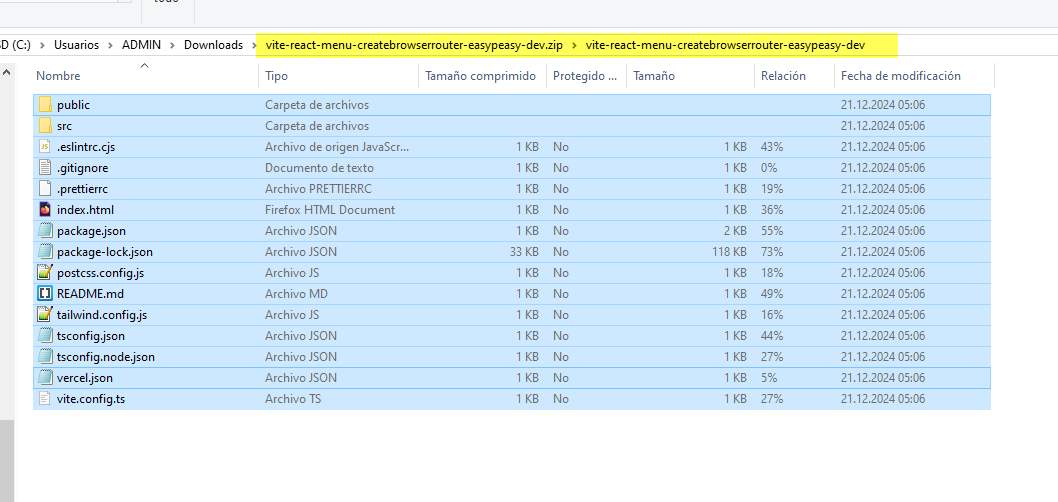
- again in your file explorer, go to your project directory and paste them in
- all files will copy over, but notice that you will overwrite your .gitignore file
- when you return to your VSCode, you will see that you have 3000+ files to check in
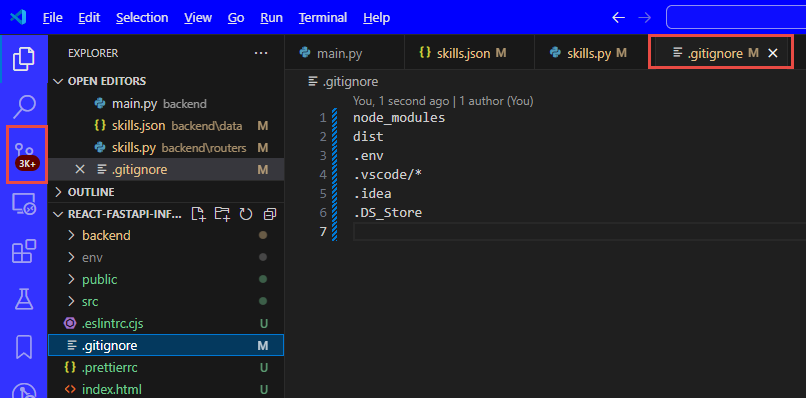
- this is because we overwrote the .gitignore file
- so add the content from the old .gitignore file to the new one, and you should then only have the 30 newly added files to check in
- >>> 5. test that frontend and backend can both run in the same directory
- in new VSCode terminal, install and start the React site
npm inpm run dev
- the frontend should open in your browser to port 3363, or if that is being used, then 3364
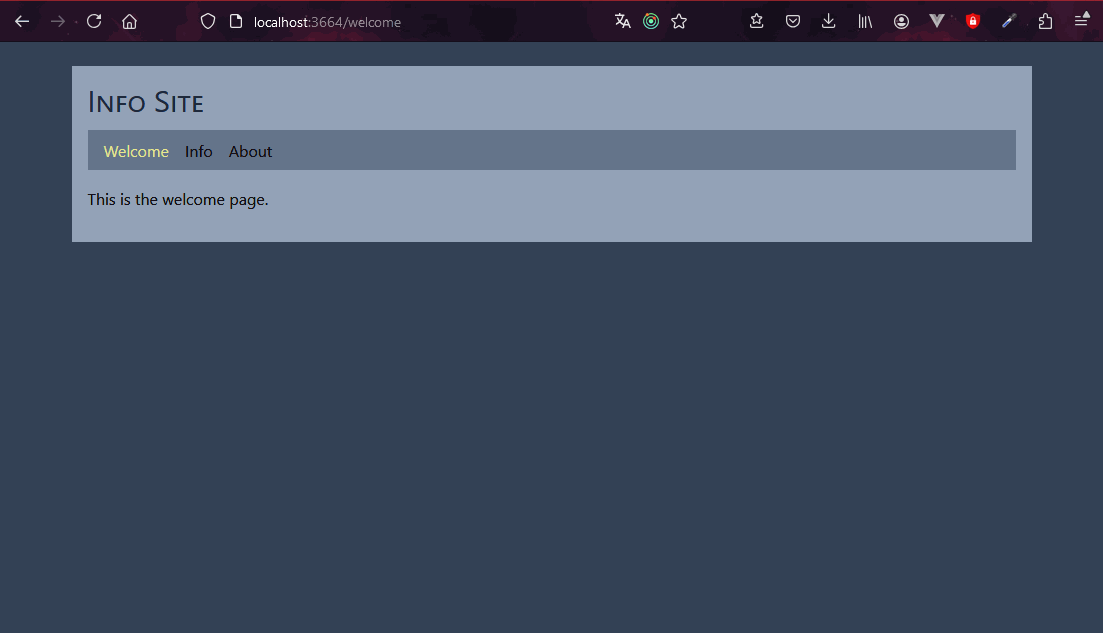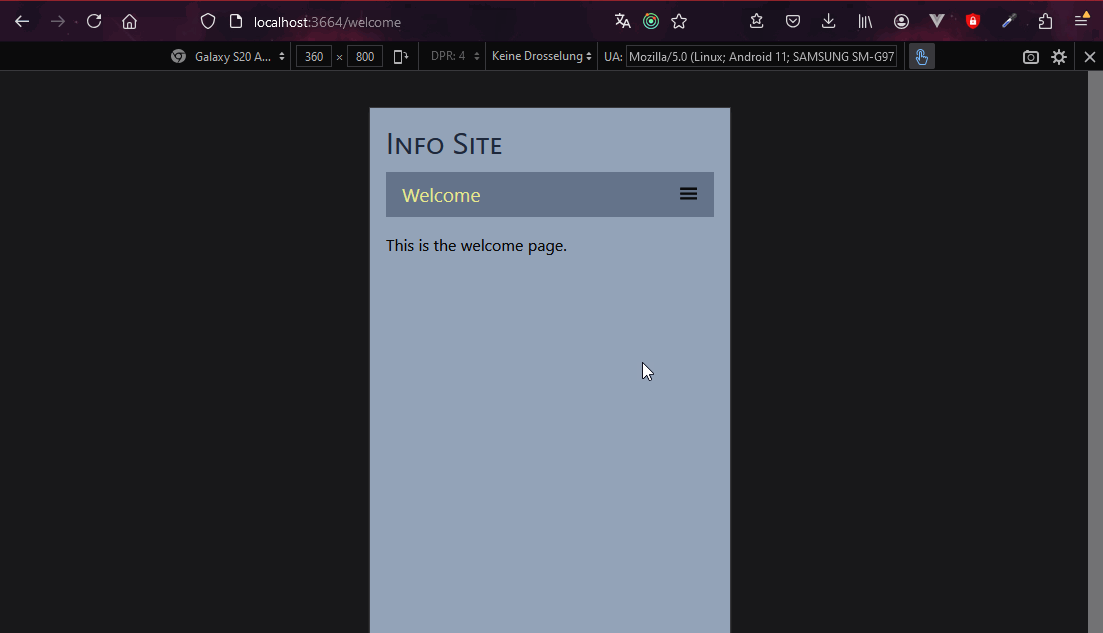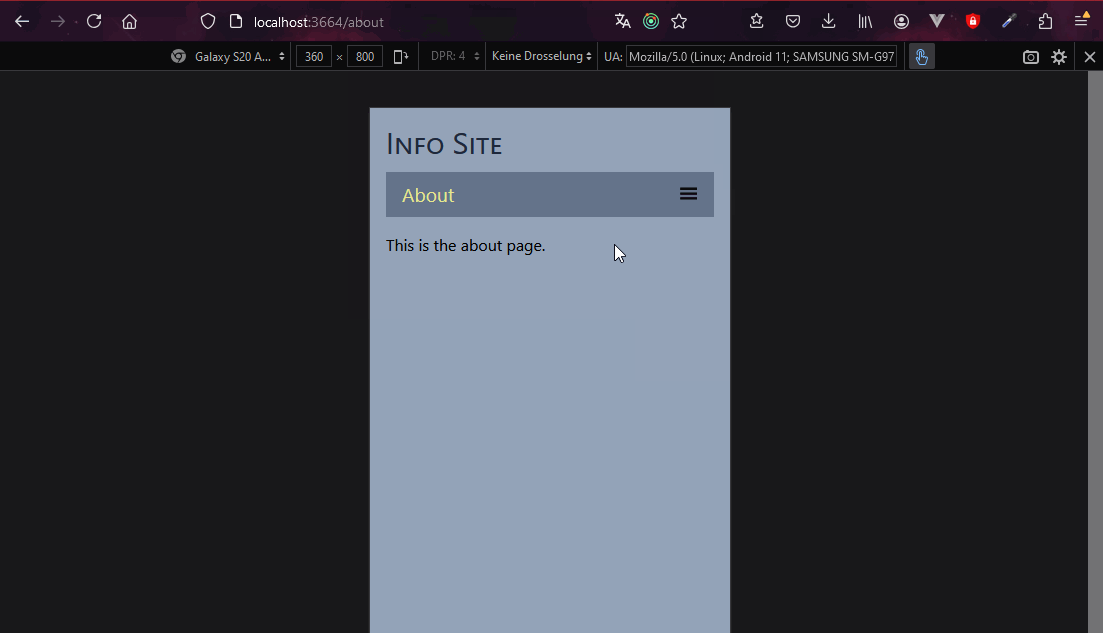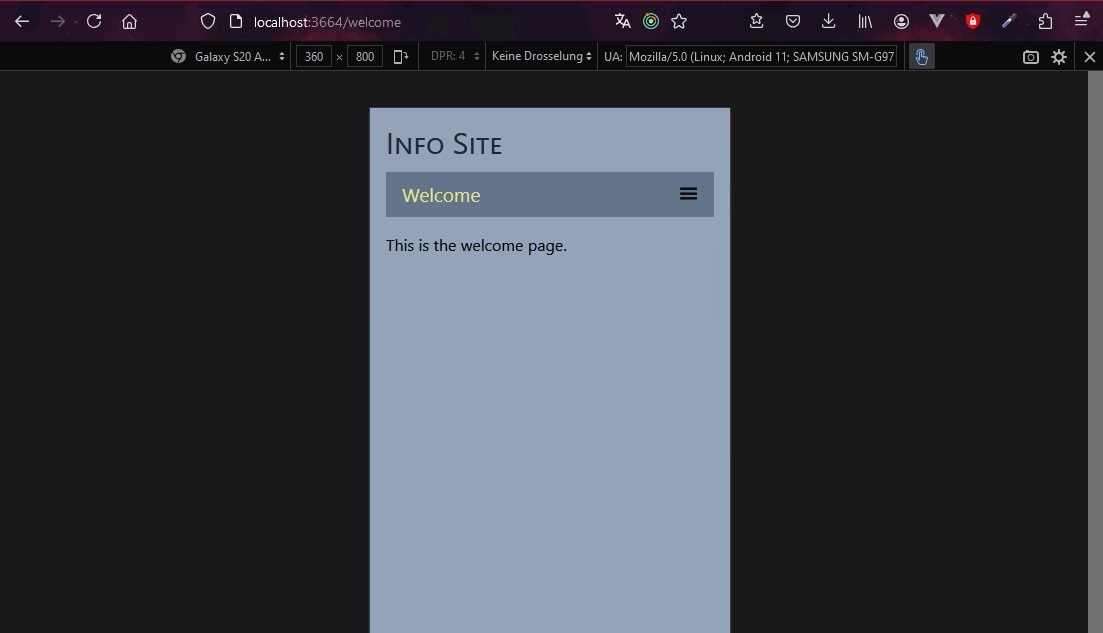
- in new VSCode terminal, install and start the React site
- >>> 6. enable the fullstack website to start with one command
- we now want to change the package.json commands so that when we type npm run dev it starts the backend and frontend at the same time
- stop both the frontend and backend and close all VSCode terminal windows
- open up a new VSCode terminal
- in package.json change the "dev" script to "frontend"
- "frontend": "vite --port 3663 --open",
- test it with
npm run frontend- it should start your site again
- stop it with CTRL-C
- now in the root directory, create a file to start the backend: start-backend.sh
- source env/Scripts/activatecd backend./serve.sh
- in package.json create a script to start the file that starts the backend:
- "backend": "bash ./start-backend.sh",
- test it with
npm run backend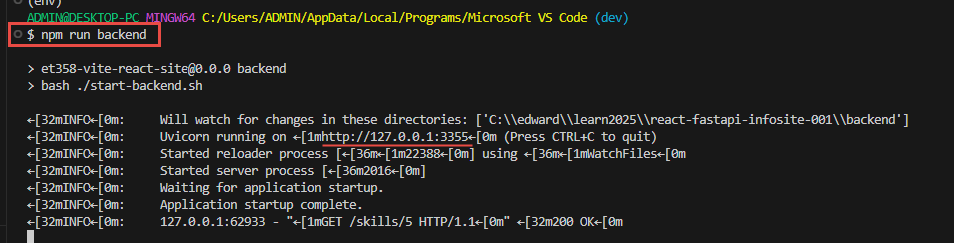
- then see if Postman can fetch the data:
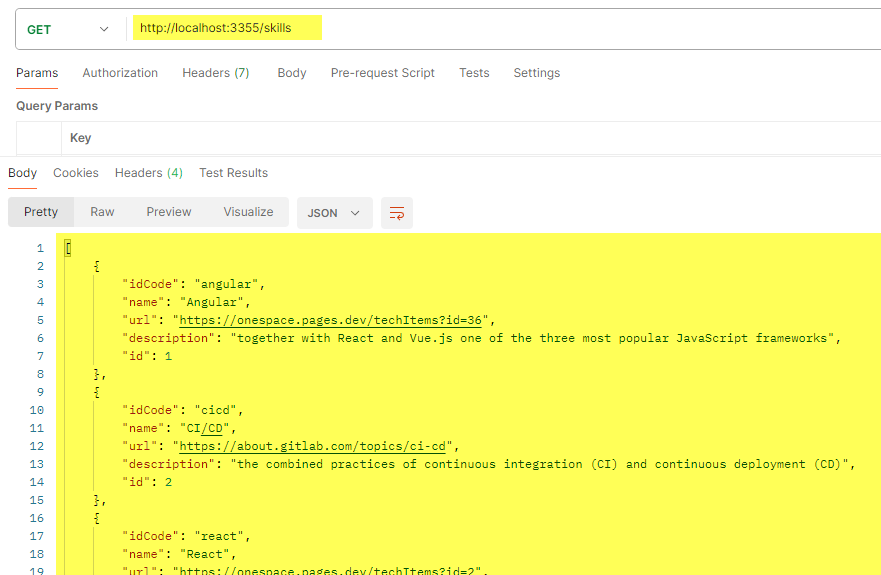
- then see if Postman can fetch the data:
- now we want to make an NPM script that starts both backend and frontend at the same time
- stop both services, close all VSCode terminal windows and open up a new VSCode terminal window
- since we need to start both frontend and backend at the same time we need to install a tool call concurrently
- install it as a development dependency:
npm i -D concurrently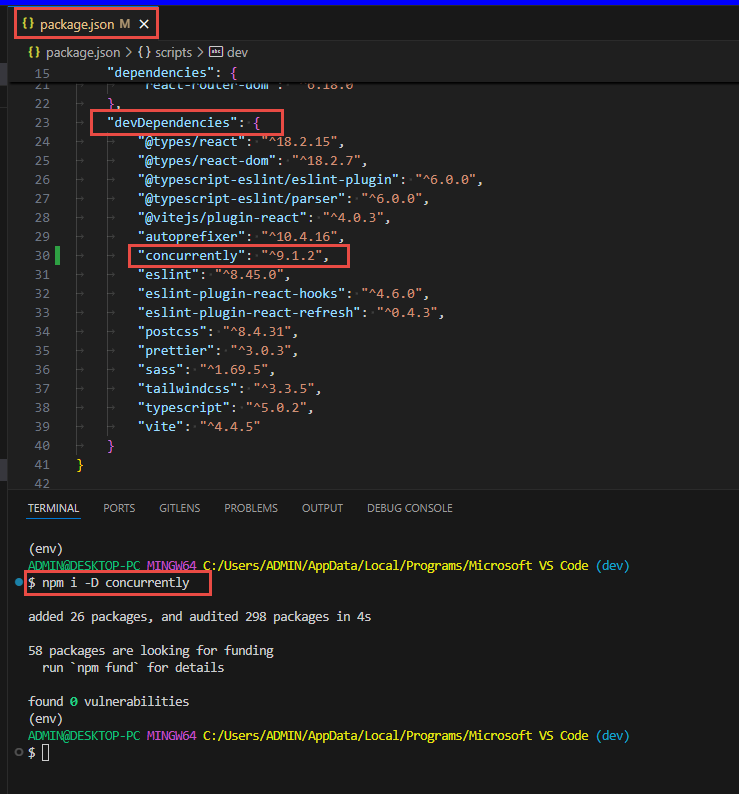
- package.json
- "dev": "conc \"npm run backend\" \"npm run frontend\"",
- now start both backend and frontend with
npm run dev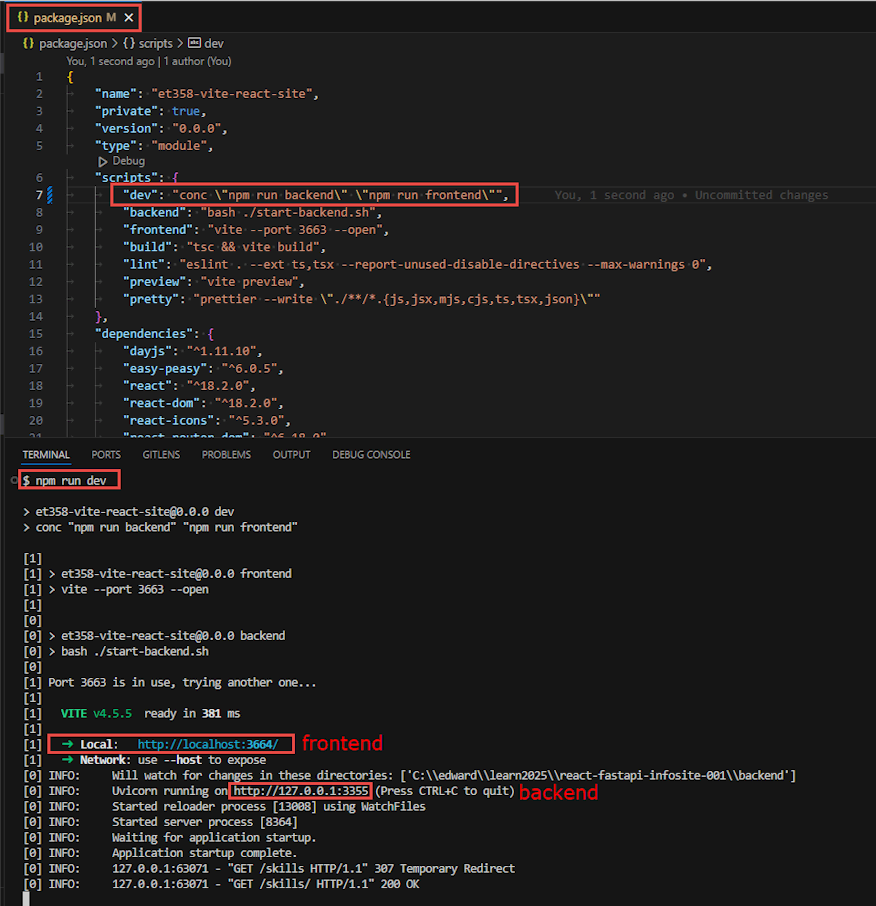
- your frontend site should be running in the browser, and your backend should be available via Postman
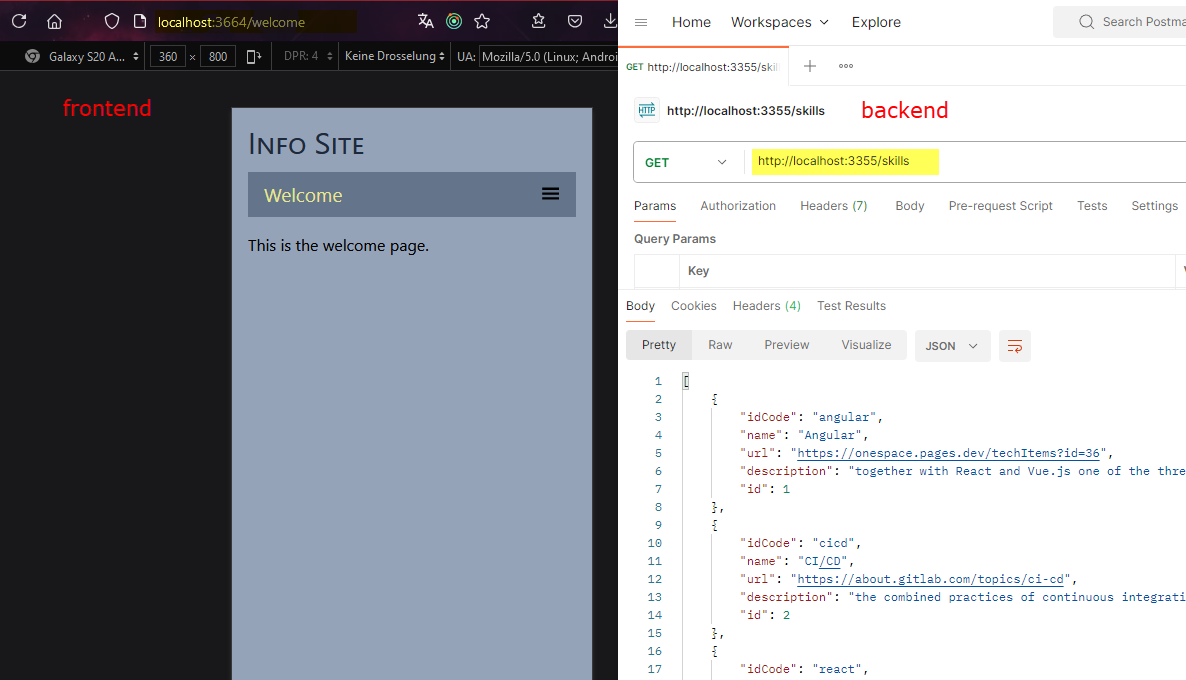
- >>> 7. in the frontend, do a simple test to fetch and display data from the backend, and resolve any CORS errors
- we ultimately want to use easy-peasy Redux to manage our data
- however, let's do this a step at a time
- we will first do a simple fetch to get all skills from the backend and display them directly on the page
- this will test if our frontend and backend can communicate at all
- I'll use axios instead of fetch, I like the simpler syntax
npm i axios
- add to PageWelcome.tsx
- useEffect(() => {(async () => {const response = await axios.get("http://localhost:3355/skills");const skills = response.data;console.log(11111, skills);})();}, []);
- when you run this, you will get a CORS error
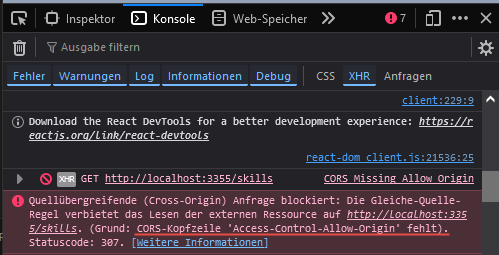
- this means we need to configure our backend's CORS parameters to allow requests from the frontend's origin
- main.py
- from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddlewareorigins = ["http://localhost:3664"]app.add_middleware(CORSMiddleware, allow_origins=origins)
- main.py
- NOTE: if you want to allow all frontend ports
- a good idea if you are using this as a local application where security is not an issue
- and the port may change is something is running on the original port
- then use this wildcard syntax:
- app.add_middleware(CORSMiddleware, allow_origins=["*"])
- when you change the above 3664 to another number, it will not work, so it along allows requests from a frontend with that URL and port
- NOTE: you might find at this point that starting both backend and frontend with concurrently leads to conflicts when the backend has to restart after a file change
- if this is the case, simply start them separately, first in one terminal:
npm run backend
- then in another terminal:
npm run frontend
- there are many CI/CD solutions to starting processes for frontend/backend
- depending on how you use the site, e.g. locally, or online
- so find and use the one that works for you
- I personally find concurrently works well for Node/Express/React fullstack sites that are in one directory
- but concurrently seems to have conflicts with the uvicorn --reload script
- if this is the case, simply start them separately, first in one terminal:
- now that you have solved the CORS issue, display your data on the page
- PageWelcome.tsx
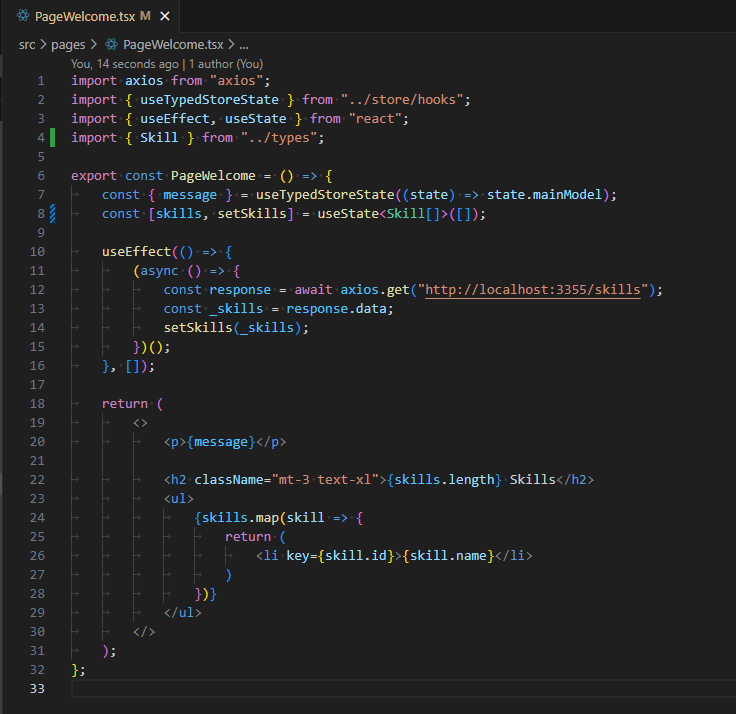
- import axios from "axios";import { useTypedStoreState } from "../store/hooks";import { useEffect, useState } from "react";export const PageWelcome = () => {const { message } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.mainModel);const [skills, setSkills] = useState([]);useEffect(() => {(async () => {const response = await axios.get("http://localhost:3355/skills");const _skills = response.data;setSkills(_skills);})();}, []);return (<><p>{message}</p><h2 className="mt-3 text-xl">{skills.length} Skills</h2></>);};
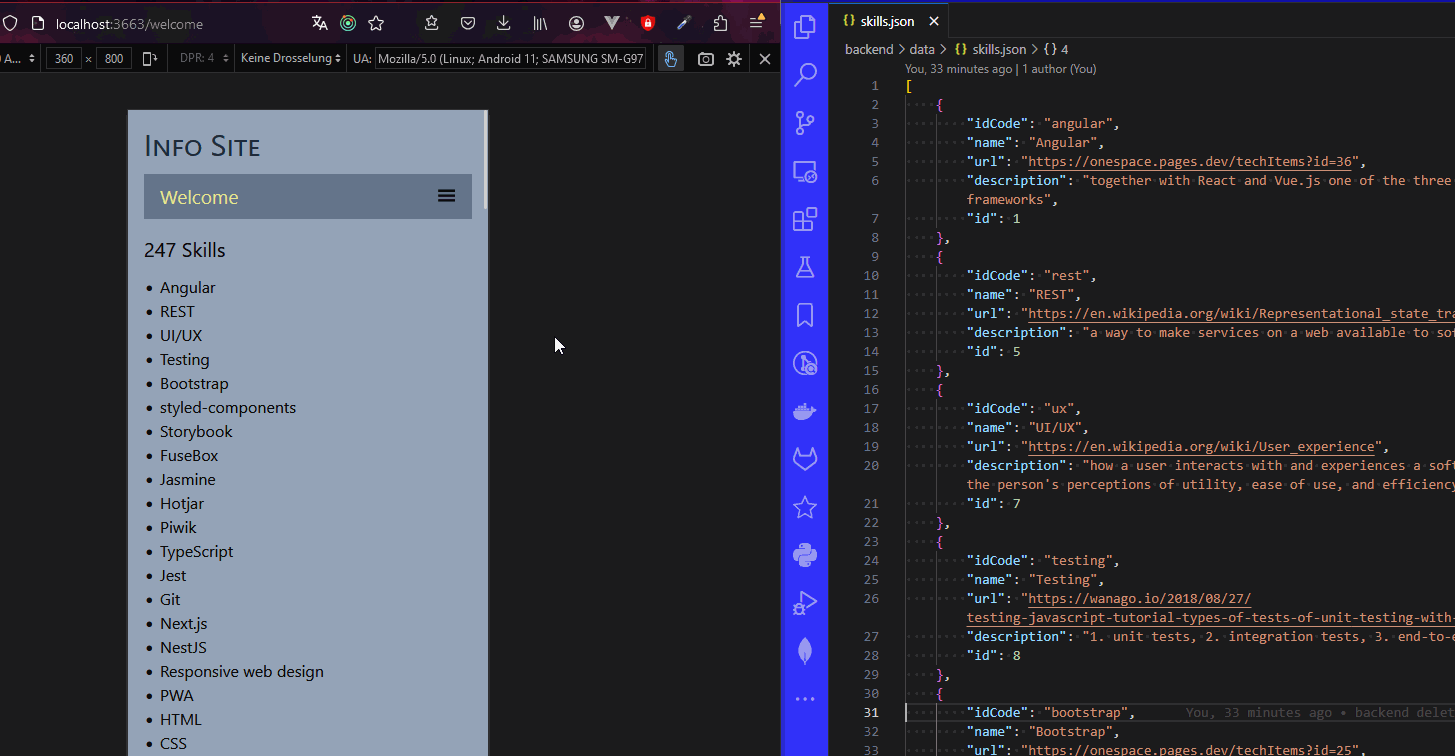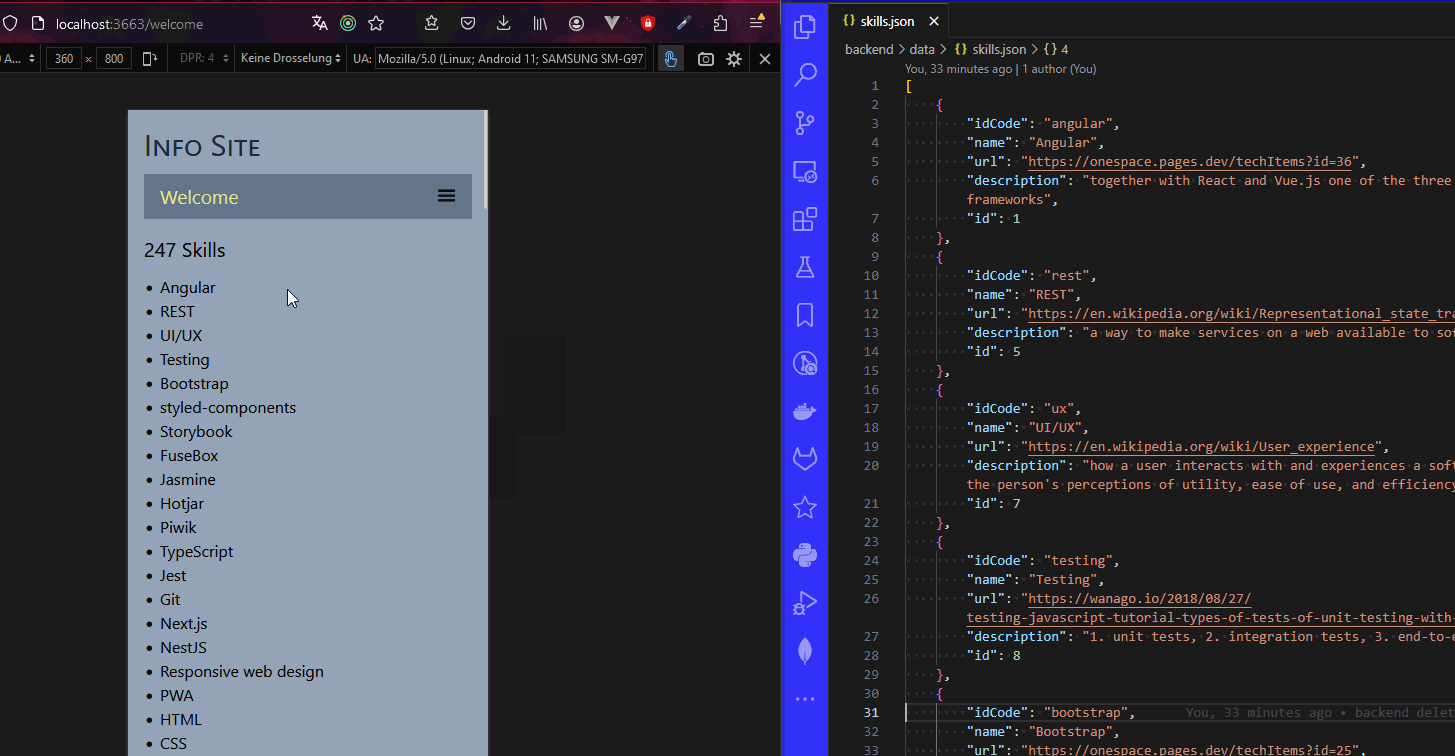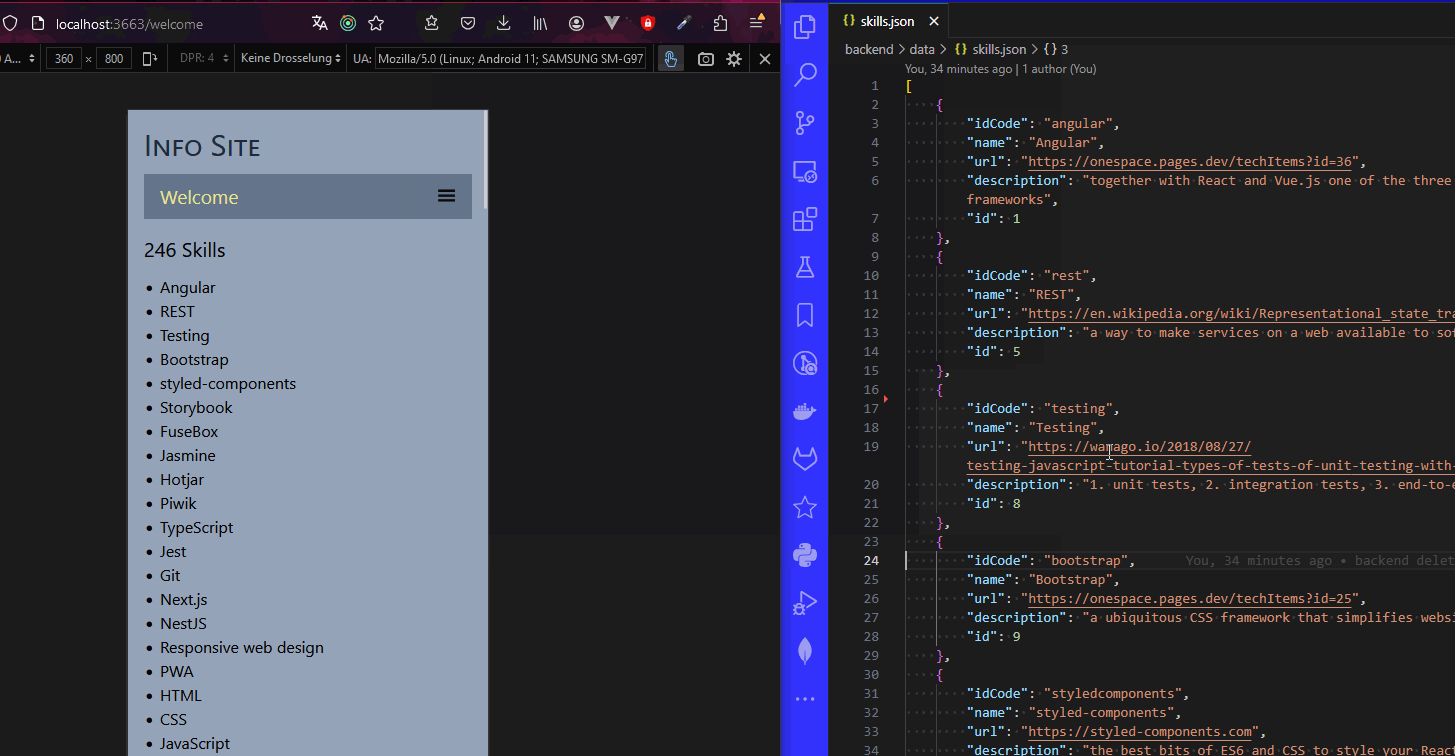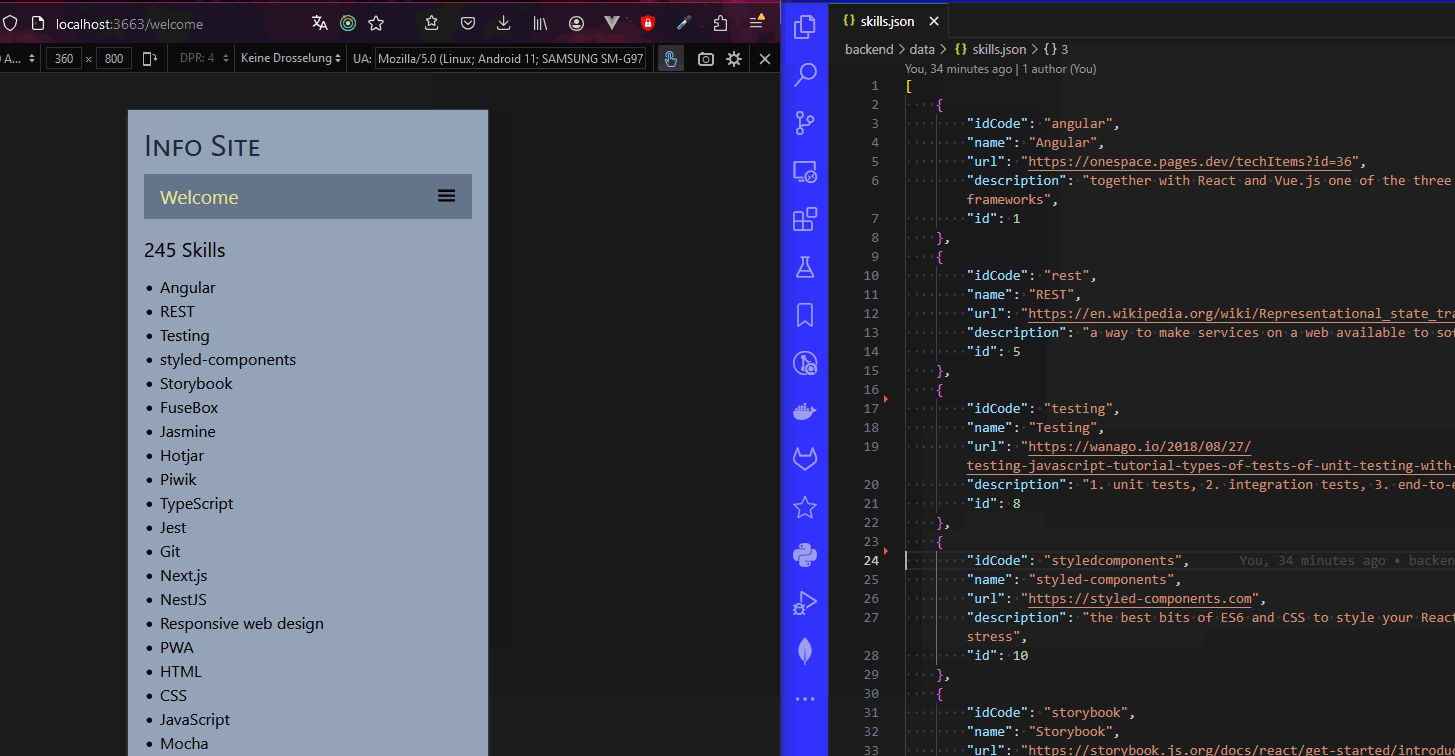
- we see that it is displaying 251 items, so now let's show them as well
- PageWelcome.tsx
- <ul>{skills.map(skill => {return (<li key={skill.id}>{skill.name}</li>)})}</ul>
- PageWelcome.tsx
- you should now see all the skills being displayed
- NOTE: our skills are not yet typed for TypeScript
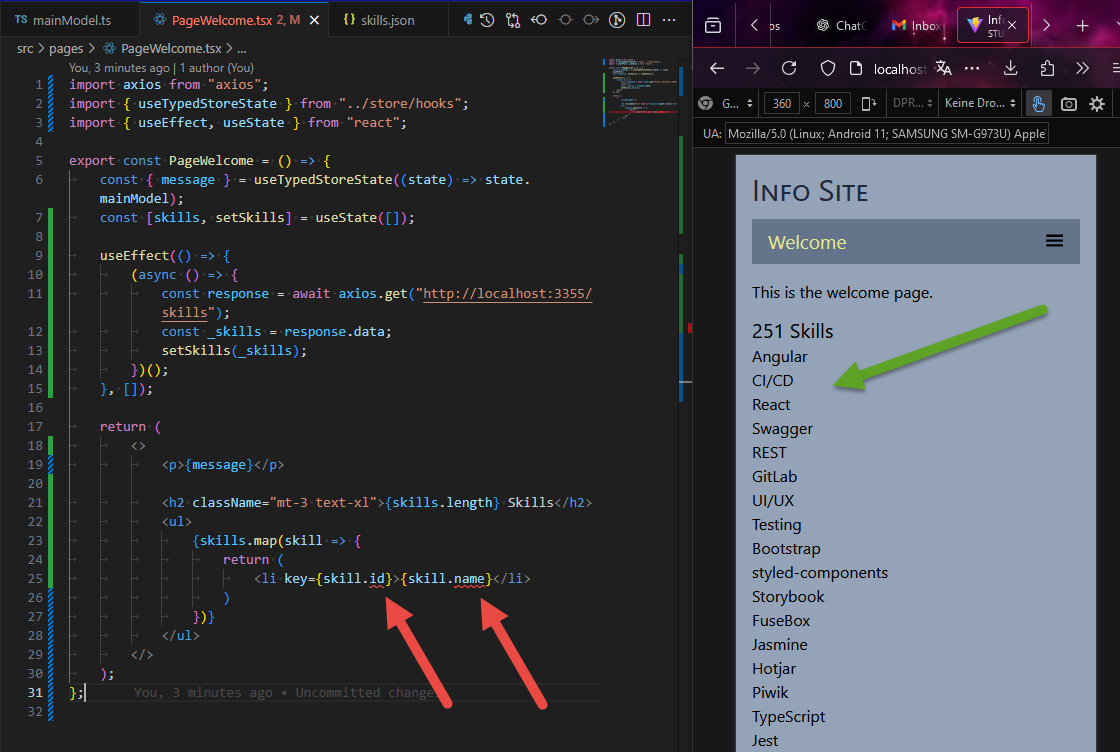
- add a TypeScript type that describes the shape of the skills
- src/types.ts
- export type Skill = {id: number;idCode: string;name: string;description: string;url: string;}
- PageWelcome.tsx
- import { Skill } from "../types";const [skills, setSkills] = useState<Skill[]>([]);
- src/types.ts
- you now have auto-completion on your Skill objects:
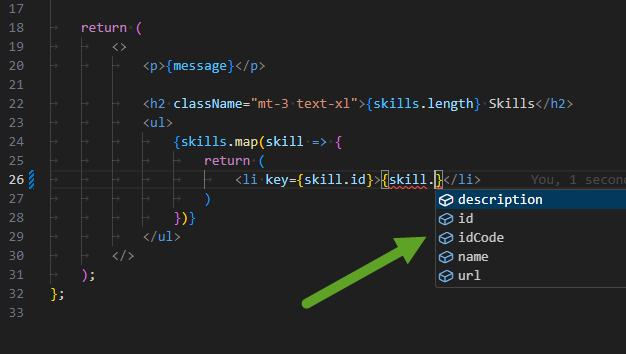
- and no more TypeScript errors:
- PageWelcome.tsx
- >>> 8. Load data centrally from an easy-peasy Redux store with mock data
- background
- for more complex applications, you want to have some kind of centralized store management besides state variables that you load on every page
- some examples are React's useContext, Zustand, Jotai and Redux
- Redux is the oldest and most complex, and has the most boilerplate, even when you use Redux Toolkit
- easy-peasy is a wrapper for Redux which simplifies it yet gives you most of its most important features
- easy-peasy is already built into the template we used for the frontend
- we will now extend it to centrally load the skills from the backend
- and on the welcome page, we will load the skills directly from the easy-peasy store, just as currently message is being loaded from the easy-peasy store:
- const { message } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.mainModel);
- create a skill model with mock data and display it on the welcome page
- src/store/models/skillModel.ts
- import { Skill } from "../../types";export interface SkillModel {// stateskills: Skill[];}export const skillModel: SkillModel = {// stateskills: [{idCode: "angular",name: "Angular",url: "https://onespace.pages.dev/techItems?id=36",description:"together with React and Vue.js one of the three most popular JavaScript frameworks",id: 1,},{idCode: "cicd",name: "CI/CD",url: "https://about.gitlab.com/topics/ci-cd",description:"the combined practices of continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD)",id: 2,},],};
- add skill model to store.ts
- import { createStore } from "easy-peasy";import { mainModel, MainModel } from "./models/mainModel";import { skillModel, SkillModel } from "./models/skillModel";export type StoreModel = {mainModel: MainModel;skillModel: SkillModel;};export const store = createStore<StoreModel>({mainModel,skillModel});
- in PageWelcome.tsx get data from the easy-peasy store instead
- import { useTypedStoreState } from "../store/hooks";export const PageWelcome = () => {const { message } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.mainModel);const { skills } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.skillModel);return (<><p>{message}</p><h2 className="mt-3 text-xl">{skills.length} Skills</h2><ul>{skills.map((skill) => {return <li key={skill.id}>{skill.name}</li>;})}</ul></>);};
- src/store/models/skillModel.ts
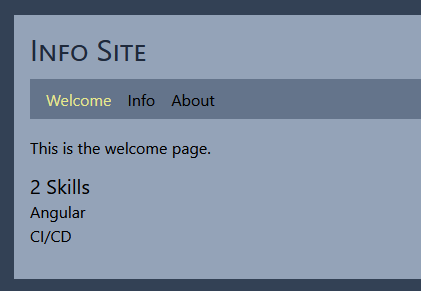
- the data will be displayed as before
- background
- >>> 9. Replace mock data with real data loaded from backend
- skillModel.ts - move the axios code from PageWelcome to our skillModel in a load thunk
- /* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any */import { action, Action, thunk, Thunk } from "easy-peasy";import { Skill } from "../../types";import axios from "axios";export interface SkillModel {// stateskills: Skill[];// actionssetSkills: Action<this, Skill[]>;// thunksloadSkillsThunk: Thunk<this>;}export const skillModel: SkillModel = {// stateskills: [],// actionssetSkills: action((state, skills) => {state.skills = structuredClone(skills);}),// thunksloadSkillsThunk: thunk((actions) => {(async () => {try {const response = await axios.get("http://localhost:3355/skills");if (response.status === 200) {const _skills: Skill[] = response.data;actions.setSkills(_skills);}} catch (e: any) {console.log(`ERROR: ${e.message}`);}})();}),};
- mainModel.ts - add the initialize thunk which loads all data for the app, currently only Skills
- import { thunk, Thunk } from "easy-peasy";import { StoreModel } from "../store";export interface MainModel {// statemessage: string;// thunksinitialize: Thunk<this, void, void, StoreModel>;}export const mainModel: MainModel = {// statemessage: "This is the welcome page.",// thunksinitialize: thunk((_, __, { getStoreActions }) => {getStoreActions().skillModel.loadSkillsThunk();}),};
- App.tsx - now initialize the store when the application loads
- import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom";import { Header } from "./components/Header";import { useTypedStoreActions } from "./store/hooks";import { useEffect } from "react";function App() {const {initialize} = useTypedStoreActions(actions => actions.mainModel);useEffect(() => {initialize();})return (<main className="bg-slate-400 p-4 w-full md:w-[60rem] mt-0 md:mt-6"><Header /><main className="py-4"><Outlet /></main></main>);}export default App;
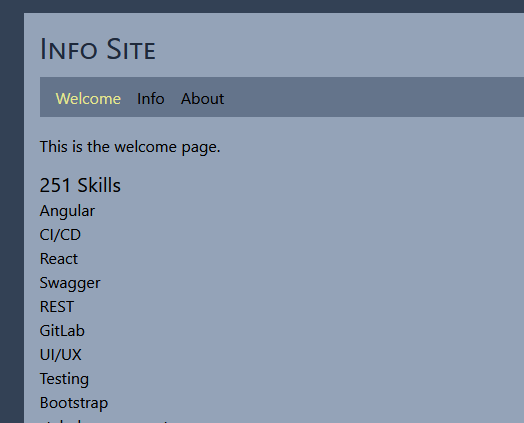
- your site now loads skills from the backend via the easy-peasy store
- skillModel.ts - move the axios code from PageWelcome to our skillModel in a load thunk
- >>> 10. Validate/cleanse data with Zod
- why validate/cleanse data
- you never want to trust fetched data even if it is data you manage yourself as in our application
- for instance, if for some reason the field on one item in your datasource is changed from "name" to "title"
- then that item will simply not appear on the frontend, but no error will be thrown, and nobody will be informed of it
- this is why you need to validate and cleanse any data being imported from external sources
- to do this, we are going to use a library called Zod which works together with TypeScript
- we will create a dataModel from which all of our data comes
- this dataModel will be responsible for providing cleaned and validated data
- if the dataModel finds unclean data (e.g. names with spaces on either side), it will clean them (trim) before passing it onto the application
- if the dataModel finds invalid data (e.g. missing fields), it will not pass that invalid item to the application, and will write in a log, notify the developer, and send an error message to the application in case the application wants to notify the user
- note that because the dataModel will be fetching data async, it needs to return not data, but promises of data
- >>> 10.1 create dataModel and get data from it
- src/store/dataModel.ts
- import axios from "axios";import { Skill } from "../types";export const getSkills = async () => {return new Promise<Skill[]>((resolve, reject) => {(async () => {try {const response = await axios.get("http://localhost:3355/skills");if (response.status === 200) {const _skills: Skill[] = response.data;resolve(_skills);}} catch (e: unknown) {reject(`ERROR: ${(e as Error).message}`);}})();});};
- skillModel.ts
- import * as dataModel from '../dataModel';loadSkillsThunk: thunk((actions) => {(async () => {const _skills = await dataModel.getSkills()actions.setSkills(_skills);})();}),
- src/store/dataModel.ts
- >>> 10.2 add Zod and validate the data
- import Zod
npm i zod
- types.ts - create TypeScript type from Zod schema
- import { z } from "zod";export const SkillSchema = z.object({id: z.number(),idCode: z.string(),name: z.string(),description: z.string(),url: z.string().url(),});export type Skill = z.infer<typeof SkillSchema>;
- dataModel.ts - add cleansing (trim each field) and validation (e.g. all field are required, url can't be empty and much be a valid url)
- import axios from "axios";import { Skill, SkillSchema } from "../types";export const getSkills = async () => {return new Promise<Skill[]>((resolve, reject) => {(async () => {try {const response = await axios.get("http://localhost:3355/skills");if (response.status === 200) {const _rawSkills: Skill[] = response.data;const _skills: Skill[] = [];for (const _rawSkill of _rawSkills) {const parseResult = SkillSchema.safeParse(_rawSkill);if (parseResult.success) {const _skill: Skill = {id: _rawSkill.id,idCode: _rawSkill.idCode.trim(),name: _rawSkill.name.trim(),description: _rawSkill.description.trim(),url: _rawSkill.url.trim(),};_skills.push(_skill);} else {let r = "";r += `INVALID SKILL IN IMPORT: ${JSON.stringify(_rawSkill,null,2)}\n`;parseResult.error.errors.forEach((err) => {r += `Error in field "${err.path.join(".")}" - ${err.message}\n`;});console.error(r);}}resolve(_skills);}} catch (e: unknown) {reject(`ERROR: ${(e as Error).message}`);}})();});};
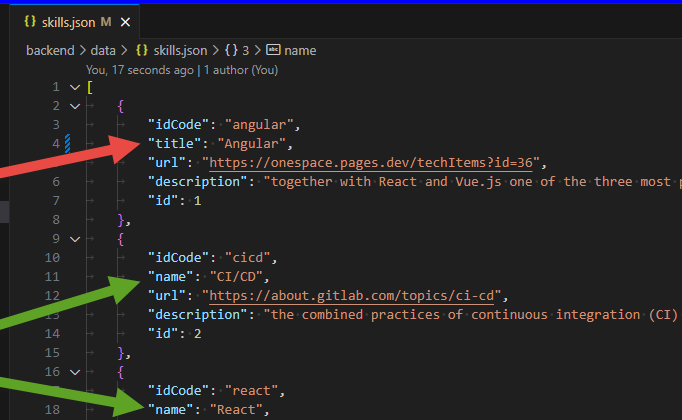
- now in skills.json change "name" to "title" for one item
- {"idCode": "angular","title": "Angular","url": "https://onespace.pages.dev/techItems?id=36","description": "together with React and Vue.js one of the three most popular JavaScript frameworks","id": 1},
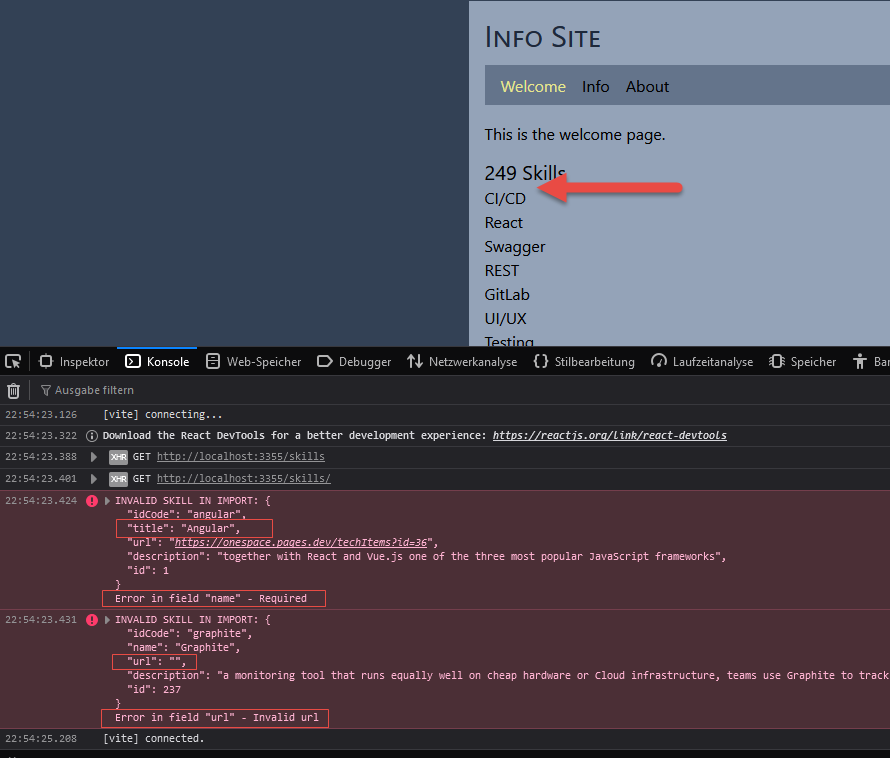
- when you load the application again, you see that Zod notified invalid items for you and removed from the array delivered to the application
- note that it found not only the name-to-title change above, but also another item which has an empty URL which is invalid
- import Zod
- why validate/cleanse data
- >>> 11. Enable user to toggle skills
- we now want the use to be able to click on a skill to see more information about it
- to do this, we need to add to each skill object a parameter named isOpen (boolean)
- with React, we can then simply toggle this boolean with a click, save the whole array back into state
- this will enable each individual item to be toggle open and closed
- first, let's correct a nuanced issue regarding our incoming data in our dataModel
- namely, we really don't know that _skills are of type Skill[], which is why we validate each one with Zod
- so more accurately, they should be typed as any
- but when using TypeScript, you should avoid using any if at all possible, cleaner coding practice would be to use unknown
- second, we have two kinds of skills, RawSkills (those coming from the JSON file) and Skills (those with the isOpen property)
- types.ts
- import { z } from "zod";export const RawSkillSchema = z.object({id: z.number(),idCode: z.string(),name: z.string(),description: z.string(),url: z.string().url(),});export const SkillSchema = RawSkillSchema.extend({isOpen: z.boolean()})export type RawSkill = z.infer<typeof RawSkillSchema>;export type Skill = z.infer<typeof SkillSchema>;
- dataModel.ts
- const _rawSkills: unknown[] = response.data;const _skills: Skill[] = [];for (const _rawSkill of _rawSkills) {const parseResult = RawSkillSchema.safeParse(_rawSkill);if (parseResult.success) {const { id, idCode, name, description, url } =parseResult.data;const _skill: Skill = {id: id,idCode: idCode.trim(),name: name.trim(),description: description.trim(),url: url.trim(),isOpen: false};_skills.push(_skill);
- note that even though we defined the incoming data as unknown[], TypeScript still knows that e.g. id is a number since it passed the Zod validation as an integer
- types.ts
- now let's display extra data (description and a "more info" link) if the skill is toggled open
- PageWelcome.tsx
- import { useTypedStoreActions, useTypedStoreState } from "../store/hooks";import { Skill } from "../types";export const PageWelcome = () => {const { skills } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.skillModel);const { saveSkill } = useTypedStoreActions((actions) => actions.skillModel);const handleToggleSkill = (skill: Skill) => {skill.isOpen = !skill.isOpen;saveSkill(skill);};return (<><h2 className="text-xl mb-3">{skills.length} Skills</h2><ul className="list-disc ml-4">{skills.map((skill) => {return (<li key={skill.id}><pclassName={`cursor-pointer w-fit ${skill.isOpen ? 'font-bold' : ''}`}onClick={() => handleToggleSkill(skill)}>{skill.name}</p>{skill.isOpen && (<div className="border border-slate-500 border-1 bg-slate-300 px-2 py-1 mb-2 w-fit rounded-md"><p>{skill.description}</p><p className="text-sm italic">get more info about{" "}<ahref={skill.url}className="underline"target="_blank">{skill.name}</a></p></div>)}</li>);})}</ul></>);};
- PageWelcome.tsx
- the skills will now click open and shut like this:
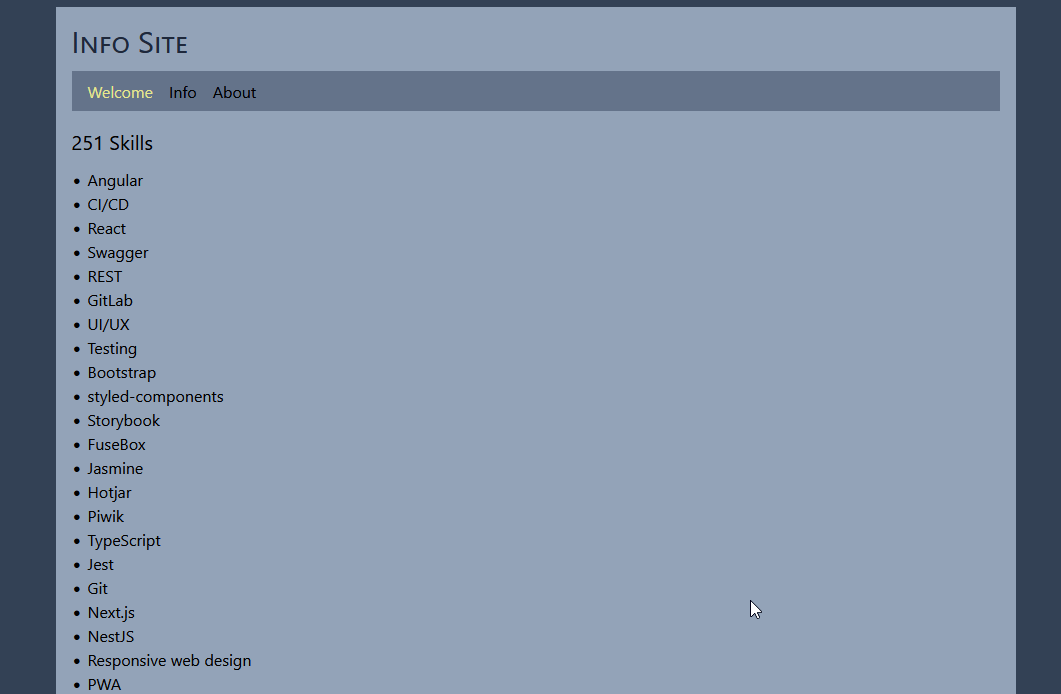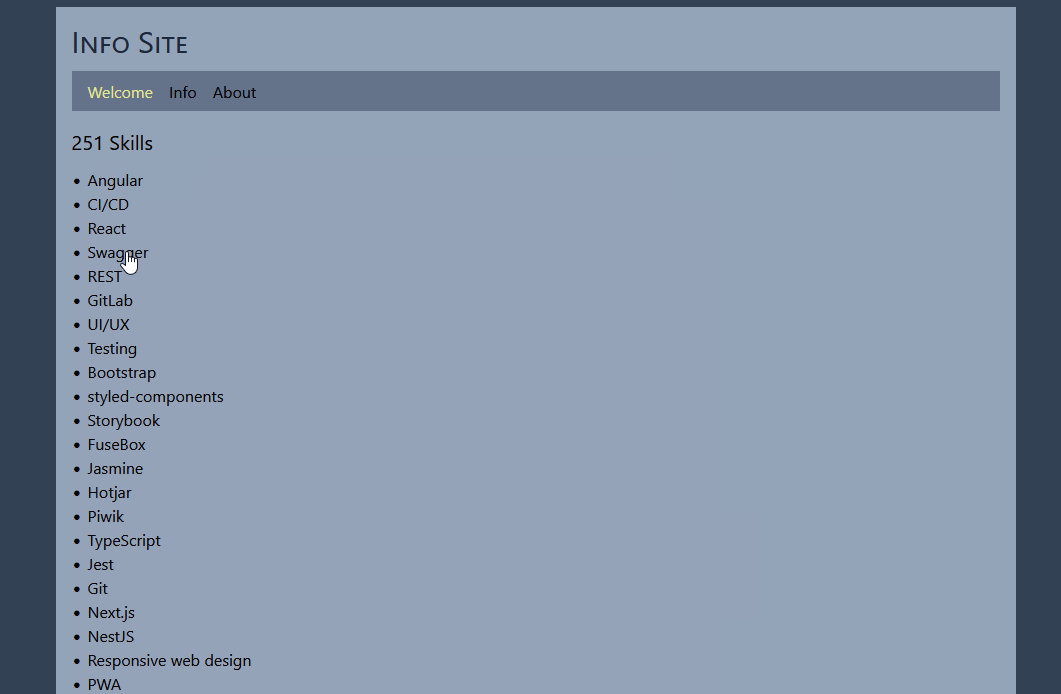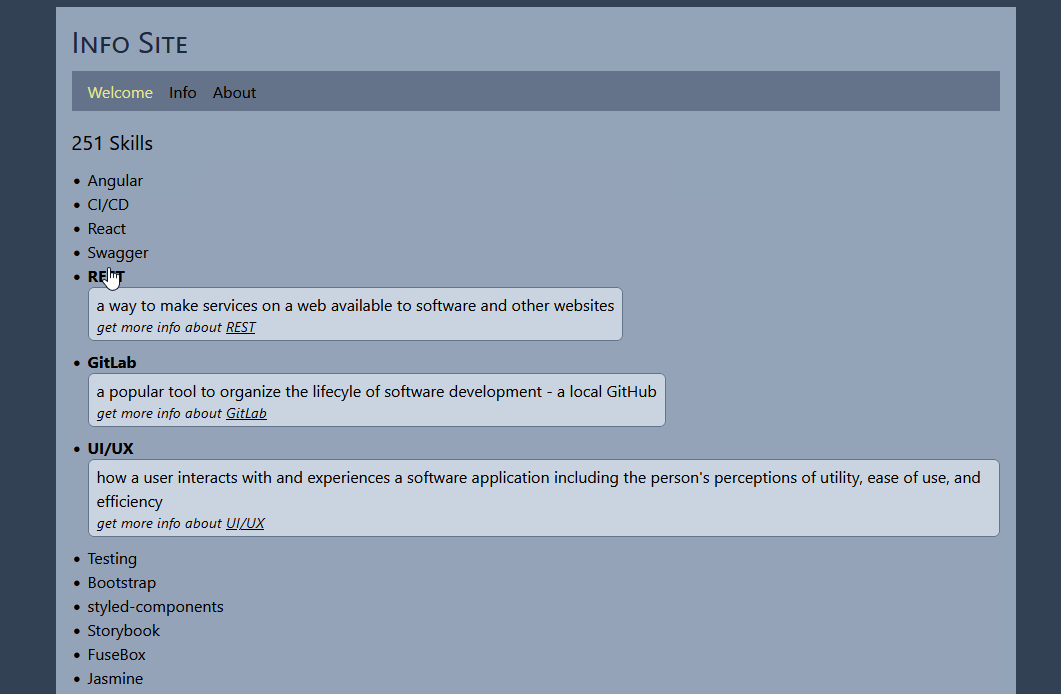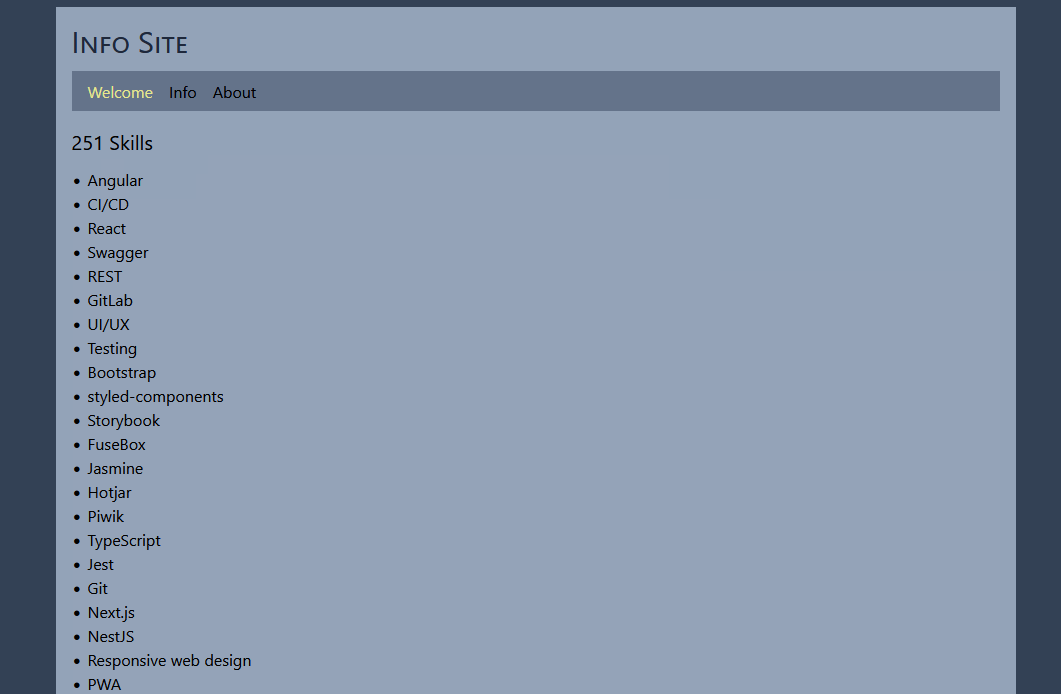
- >>> 12. Enable user to delete skills
- we will now create a delete button for each skill so the user can delete skills
- >>> 12.1 Create a delete route on the backend
- add to skills.py
- from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse@router.delete("/{id}")async def delete_skill(id: int):with open("data/skills.json", "r") as file:skills = json.load(file)skill_to_delete = next((skill for skill in skills if skill["id"] == id), None)if not skill_to_delete:raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_404_NOT_FOUND, detail="Skill not found")skills = [skill for skill in skills if skill["id"] != id]with open("data/skills.json", "w") as file:json.dump(skills, file, indent=4)return JSONResponse(content={"deleted": skill_to_delete}, status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK)
- test this route with Postman
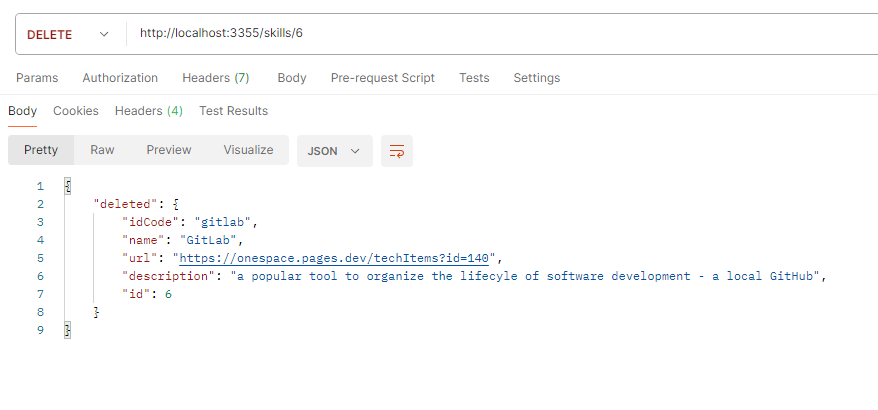
- add to skills.py
- >>> 12.2 Add delete button on each skill which calls the backend route to delete the skill
- PageWelcome.tsx
- import { useTypedStoreActions, useTypedStoreState } from "../store/hooks";import { Skill } from "../types";export const PageWelcome = () => {const { skills } = useTypedStoreState((state) => state.skillModel);const { saveSkill, deleteSkill } = useTypedStoreActions((actions) => actions.skillModel);const handleToggleSkill = (skill: Skill) => {skill.isOpen = !skill.isOpen;saveSkill(skill);};const handleDeleteSkill = (skill: Skill) => {deleteSkill(skill);};return (<><h2 className="text-xl mb-3">{skills.length} Skills</h2><ul className="list-disc ml-4">{skills.map((skill) => {return (<li key={skill.id}><pclassName={`cursor-pointer w-fit ${skill.isOpen ? "font-bold" : ""}`}onClick={() => handleToggleSkill(skill)}>{skill.name}</p>{skill.isOpen && (<div className="border border-slate-500 border-1 bg-slate-300 px-2 py-1 mb-2 w-fit rounded-md"><p>{skill.description}</p><p className="text-sm italic">get more info about{" "}<ahref={skill.url}className="underline"target="_blank">{skill.name}</a></p><div className="flex justify-end"><buttononClick={() =>handleDeleteSkill(skill)}className="">delete</button></div></div>)}</li>);})}</ul></>);};
- index.scss
- @layer base {h1 {font-variant: small-caps;}button {@apply bg-gray-400 text-white font-bold py-1 px-2 rounded hover:bg-gray-500;}}
- skillModel.ts
- /* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any */import { action, Action, thunk, Thunk } from "easy-peasy";import { Skill } from "../../types";import * as dataModel from "../dataModel";import axios from "axios";export interface SkillModel {// stateskills: Skill[];// actionssetSkills: Action<this, Skill[]>;saveSkill: Action<this, Skill>;_deleteSkill: Action<this, Skill>;// thunksloadSkillsThunk: Thunk<this>;deleteSkill: Thunk<this, Skill>;}export const skillModel: SkillModel = {// stateskills: [],// actionssetSkills: action((state, skills) => {state.skills = structuredClone(skills);}),saveSkill: action((state, skill) => {const index = state.skills.findIndex((s) => s.id === skill.id);if (index !== -1) {state.skills[index] = structuredClone(skill);}}),_deleteSkill: action((state, skill) => {const index = state.skills.findIndex((s) => s.id === skill.id);if (index !== -1) {state.skills.splice(index, 1);}}),// thunksloadSkillsThunk: thunk((actions) => {(async () => {const _skills = await dataModel.getSkills();actions.setSkills(_skills);})();}),deleteSkill: thunk((actions, skill) => {actions._deleteSkill(skill);try {(async () => {const response = await axios.delete(`http://localhost:3355/skills/${skill.id}`);if (response.status === 200) {console.log("Skill deleted successfully");} else {console.error("Failed to delete the skill");}})();} catch (error) {console.error("Error deleting skill:", error);}}),};
- main.py
- app.add_middleware(CORSMiddleware, allow_origins=["*"], allow_methods=["*"])
- PageWelcome.tsx
- the user can now delete items like this:
